Latest News
How Nutrition Smart Farming Fights Hidden Hunger and Climate Change

{ Nutrition Smart Farming – As the world commemorates another World Environment Day, the call for urgent, collective action toward a sustainable and equitable future has never been more critical. Among the most interconnected and pressing challenges we face today are hidden hunger and climate change—dual threats that quietly erode global health, food security, and environmental stability. }
While climate change disrupts agricultural productivity and reduces the nutritional content of staple crops, hidden hunger—the deficiency of essential vitamins and minerals—affects over three billion people worldwide. Together, these crises not only strain food systems but also perpetuate cycles of poverty and disease, especially in developing countries like India.

The Silent Crisis: Hidden Hunger in a Changing Climate
Hidden hunger remains an invisible epidemic. Unlike overt hunger, it doesn’t always manifest in empty stomachs but in bodies starved of crucial micronutrients like zinc, iron, and vitamin A. According to global estimates, it costs the economy a staggering $3.5 trillion annually in lost productivity and increased healthcare expenses.
India is among the worst-affected countries. The 2023 State of Food Security and Nutrition report revealed that 2.4 billion people globally face food insecurity, including 900 million experiencing severe hunger. In India, nearly a third of the world’s stunted children reside, and a shocking 300 million Indians (22% of the population) suffer from zinc deficiency. Among children under five, this number climbs to 44%, resulting in weakened immunity and increased vulnerability to diseases such as diarrhoea and pneumonia.
At the root of this crisis is depleted soil health. Over 40% of soil samples in India show zinc deficiency. Climate change is exacerbating the situation further, with rising CO₂ levels projected to reduce micronutrient content in staple crops like wheat and rice by 3–17%.
A Sustainable Solution: Nutrition Smart Farming
Traditional approaches to malnutrition have focused on food fortification and supplementation, but these are often short-term fixes. A more holistic and lasting solution lies in nutrition smart farming —an approach that enhances both the yield and nutritional quality of food while promoting environmental sustainability.
One promising example is the “Sustainable Nutri-Farms” pilot project across six districts in Uttar Pradesh, initiated in collaboration with HarvestPlus Solutions and the National Institute of Agricultural Extension Management (MANAGE). This initiative introduced biofortified wheat varieties rich in zinc and iron, alongside micronutrient-rich fertilizers and climate-resilient farming techniques.
The results were compelling. The biofortified wheat varieties contained 30.2 ppm zinc and 35.4 ppm iron, compared to 20.9 ppm zinc and 32.6 ppm iron in conventional strains—significant boosts in nutrients vital for immune function, cognitive development, and overall health.
In terms of productivity, farmers reported up to 29.33% yield increases and 42% income growth, thanks to premium pricing for the nutrient-dense grain. Adoption rates for biofortified wheat varieties rose by 87%, reflecting a strong shift in farmer mindset and confidence in sustainable practices.
Why It Works: Building Resilience from the Ground Up
Nutrition-smart agriculture works because it integrates science, soil health, and human health. Unlike top-down interventions, this model empowers farmers through knowledge-sharing, capacity building, and access to improved seeds and inputs. It also aligns closely with market demands for sustainable, high-quality food.
By restoring soil fertility and enriching staple crops with vital micronutrients, we address hidden hunger at its roots—literally. Importantly, this approach also builds resilience against climate shocks, enabling farmers to produce more with fewer resources, while reducing the environmental footprint of agriculture.
The Road Ahead: From Innovation to Implementation
With less than five years left to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goal of Zero Hunger by 2030, the stakes are high. While conventional methods show limited results, nutrition smart farming is emerging as a scalable, cost-effective alternative.
Yet scaling these solutions requires collaboration across governments, research institutions, private sector stakeholders, and farming communities. Policies must support agronomic biofortification, invest in extension services, and enable access to affordable, nutrient-enriched seeds and fertilizers.
As climate challenges intensify, nutrition smart farming offers a blueprint for transforming food systems into vehicles of resilience and recovery. It’s a practical, science-backed approach that delivers triple wins: healthier people, wealthier farmers, and a healthier planet.
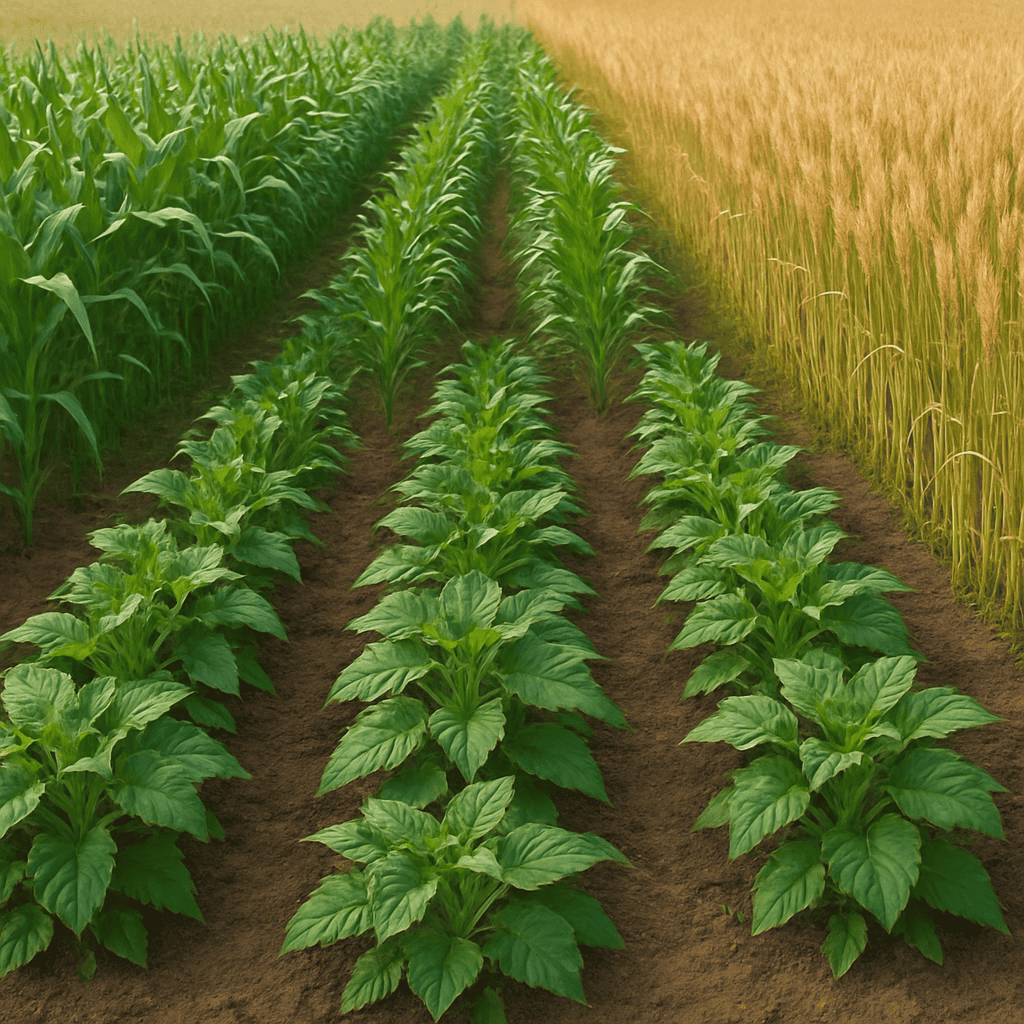

A nutrition-rich cultivation field showcasing integrated crop farming — combining leafy greens, corn, and wheat to promote soil health and address micronutrient deficiencies.
Conclusion: Nourishing the Planet One Farm at a Time
The fight against hidden hunger and climate change is not one of isolated solutions but of integrated action. Nutrition smart farming is not merely an innovation—it is an imperative.
By leveraging the power of biofortified crops, sustainable inputs, and knowledge-driven farming, we can turn today’s agricultural systems into engines of nutritional security and climate resilience. Whether it’s a smallholder farm in rural India or a policymaker’s desk in New Delhi, the time for action is now.
Let this World Environment Day be a renewed call to nourish not just our bodies, but also our soils, ecosystems, and communities—one farm, one seed, and one harvest at a time.