Creative Ideas
Agriculture Waste Recycling: Methods, Benefits, and Real-World Applications
Published
9 months agoon
By
Harish D M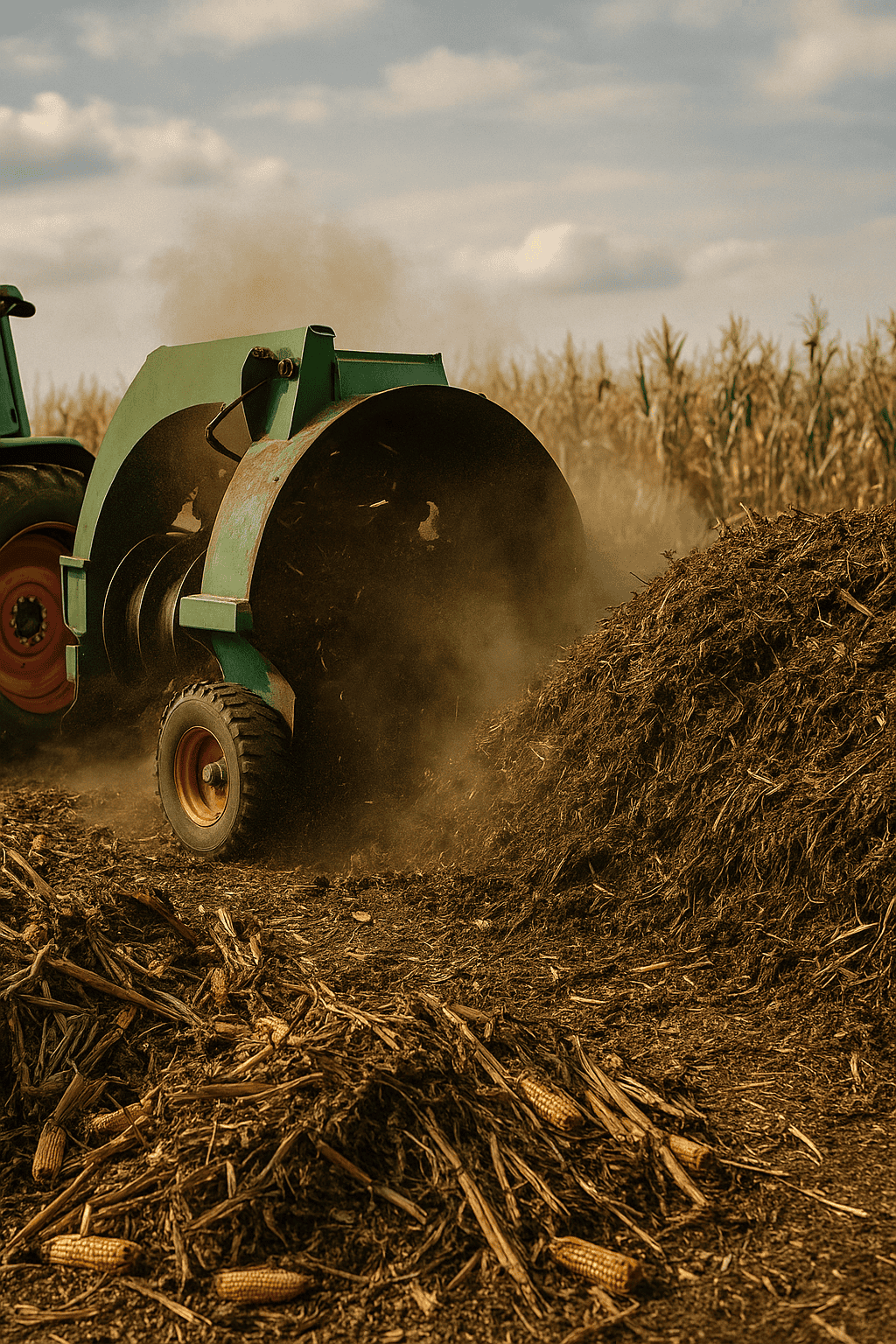
{ Agriculture Waste Recycling – Agriculture is one of the most crucial pillars of the Indian economy, but it also generates a significant amount of waste. Crop residues, animal manure, food processing by-products, and other organic materials often go unused or are burned, contributing to pollution and environmental degradation. Fortunately, Agriculture Waste Recycling offers a sustainable solution by transforming this “trash” into “treasure.” This eco-friendly approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also opens up exciting economic opportunities. }
In this blog post, we explore the top methods of agricultural waste recycling, along with their benefits and practical examples.

1. Composting: Nature’s Way of Agriculture Waste Recycling
What it is:
Composting is a natural biological process where microorganisms break down organic waste—like crop residues and manure—into nutrient-rich compost that can be used as a soil conditioner.
Benefits:
-
Improves soil fertility and texture
-
Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers
-
Minimizes the volume of organic waste sent to landfills
Examples:
-
Paddy straw, sugarcane bagasse, and kitchen waste from farm households can all be composted.
-
The resulting compost helps improve crop yields and reduces the dependence on synthetic inputs.
2. Anaerobic Digestion: Turning Waste into Biogas
What it is:
Anaerobic digestion involves breaking down organic matter in oxygen-free environments, producing biogas (a renewable source of energy) and digestate (a high-quality organic fertilizer).
Benefits:
-
Generates clean energy that can be used for cooking or electricity
-
Reduces harmful methane emissions from open manure
-
Converts waste into a dual-use product (energy + fertilizer)
Examples:
-
Gobar gas plants in rural India use cow dung and food waste to produce biogas.
-
Crop residues such as maize stalks and wheat straw can be co-digested with manure.
3. Bioenergy Production: Fuel from the Farm
What it is:
This method converts agricultural waste into energy forms like electricity, bioethanol, or biodiesel by combustion or fermentation.
Benefits:
-
Decreases reliance on fossil fuels
-
Adds new revenue streams for farmers
-
Encourages rural energy self-sufficiency
Examples:
-
Biomass power plants use rice husks, corn stalks, and cotton stems as fuel.
-
Ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse is a booming sector in India.
4. Industrial Utilization: Waste as Raw Material
What it is:
Agricultural waste can also be used in industries as a raw material for manufacturing textiles, paper, packaging, and construction materials.
Benefits:
-
Reduces the need for virgin materials
-
Drives sustainable manufacturing practices
-
Diversifies the utility of farm by-products
Examples:
-
Jute and cotton waste is used in the handmade paper industry.
-
Rice husk ash is used in cement production.
-
Corn cobs are repurposed into particle boards and biodegradable cutlery.
5. Other Innovative Applications
Beyond energy and industry, agricultural waste is now being utilized in a variety of innovative, value-added applications:
-
Biosorbents: Some crop residues can absorb pollutants from wastewater, making them useful for environmental cleanup.
-
Animal Feed: De-oiled seed cakes and fruit peels are rich in nutrients and can be turned into cost-effective animal feed.
-
Mushroom Cultivation: Paddy straw and sawdust serve as an ideal substrate for growing edible mushrooms.
-
Fortified Rice Analogues: Broken rice and bran can be transformed into nutrient-enriched food supplements.
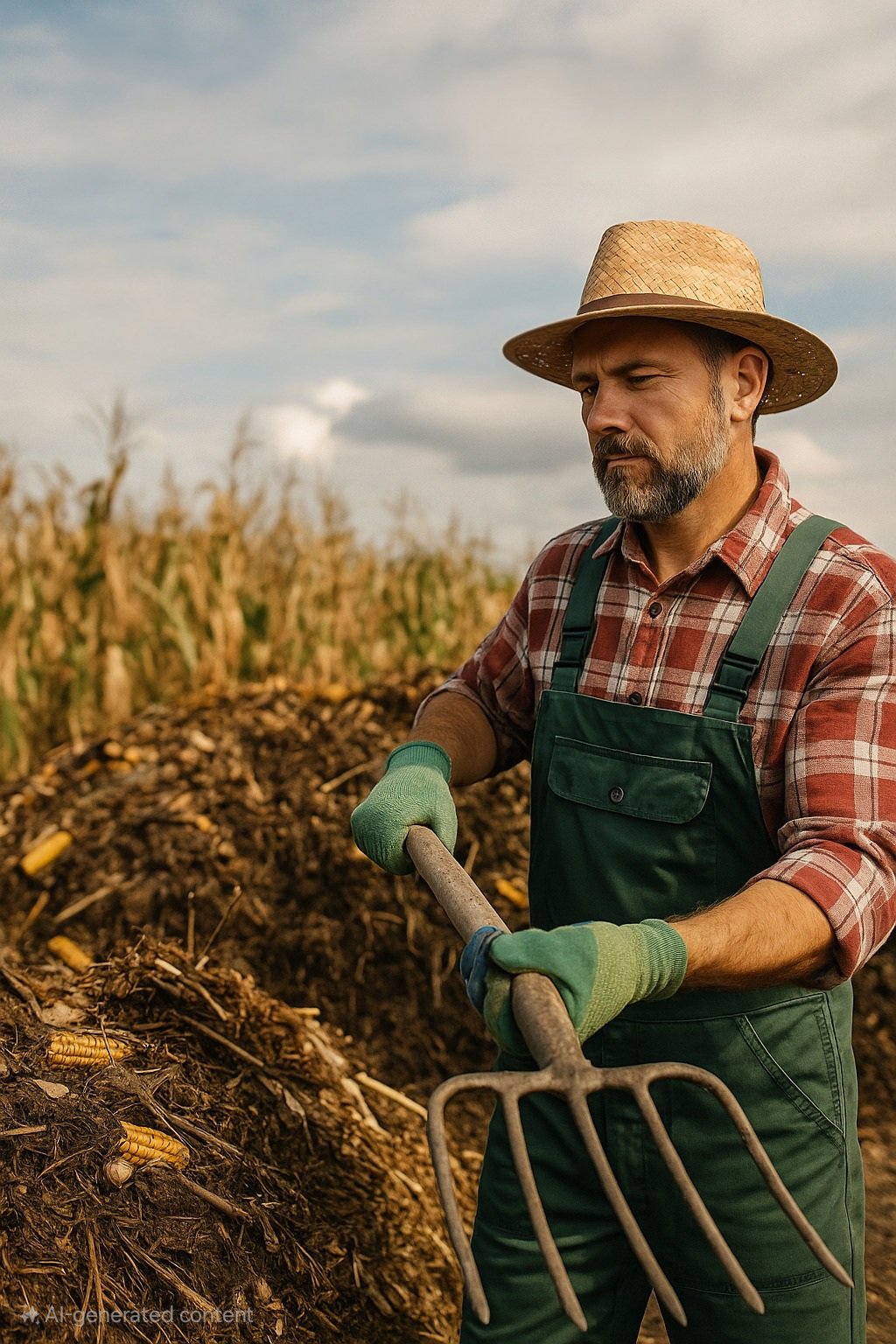

A clean, high-intent view of agricultural waste being transformed into compost — showcasing eco-friendly farming practices that convert waste into valuable resources.
Benefits of Agricultural Waste Recycling
Environmental Benefits
-
Reduces air, water, and soil pollution
-
Helps mitigate climate change by lowering methane emissions
-
Promotes biodiversity by improving soil health
Economic Benefits
-
Cuts down on waste disposal costs
-
Creates additional revenue streams
-
Lowers dependency on costly inputs like chemical fertilizers and fossil fuels
Social Benefits
-
Enhances livelihoods for farmers and rural communities
-
Boosts food security by improving soil and crop productivity
-
Encourages environmental stewardship and awareness
Q&A Section: Common Questions on Agricultural Waste Recycling
Q1: Is agricultural waste recycling feasible for small-scale farmers?
A: Yes, even small farms can benefit. Simple compost pits, low-cost biogas units, and DIY mushroom cultivation kits make it easy and affordable.
Q2: How can farmers get started with Agriculture Waste Recycling-to-energy solutions?
A: Many state and central government schemes support biogas and bioenergy projects. Start by contacting your local agricultural extension office or Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK).
Q3: Can recycling waste really improve farm profits?
A: Absolutely. By converting waste into inputs like compost and energy, farmers reduce input costs and can sell surplus products like bioenergy, mushrooms, or animal feed.
Q4: What government incentives are available?
A: Programs like the National Biogas and Manure Management Programme (NBMMP) and support under MNRE provide financial aid and technical support for bio-waste management systems.
Conclusion: Transforming Agriculture Waste Recycling into Wealth
Recycling agricultural waste is not just an environmental necessity—it’s an economic opportunity. From composting to industrial applications, each method holds the potential to improve sustainability, generate income, and build a circular farming economy. For a greener, more profitable future, it’s time Indian agriculture embraces waste recycling in all its forms.


India GDP Growth 7.6% in FY26: New GDP Series Upgrades Growth but Lowers Economy Size

India Missing Out on Big Agriculture Export Opportunity: Path to $100 Billion by 2030

ಮ್ಯೂಚುವಲ್ ಫಂಡ್ SIP ಮೂಲಕ 15 ವರ್ಷಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ₹10 ಕೋಟಿ ರೂಪಾಯಿ ಗಳಿಸುವುದು ಹೇಗೆ?

Aadhar Model Smart Card To Farmers: ರೈತರಿಗೆ ಆಧಾರ್ ಮಾದರಿ ಸ್ಮಾರ್ಟ್ ಕಾರ್ಡ್ ಯೋಜನೆ – ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣ ಮಾಹಿತಿ, ಅನುಕೂಲತೆಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ನೋಂದಣಿ ವಿವರಗಳು

ಕೇಂದ್ರ ಬಜೆಟ್ 2026 ಕೃಷಿಕರಿಗೆ ಏನು ಕೊಡುಗೆ? ಭಾರತ್ ವಿಸ್ತಾರ್ AI ಪರಿಕರದಿಂದ ರೈತರಿಗೇನು ಲಾಭ?

Farming: ಹಳ್ಳಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಹಿಂದಿರುಗಿ ಕೃಷಿಯತ್ತ ಒಲವು ತೋರುತ್ತಿರುವ ವೃತ್ತಿಪರರು – ನಿಜವಾದ ಕಾರಣಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಭವಿಷ್ಯದ ಜೀವನಶೈಲಿ

What Is the Best Climate for Saffron Cultivation?
ಕಾವೇರಿ 2.0 ಆಸ್ತಿ ನೋಂದಣಿ: 10 ನಿಮಿಷದಲ್ಲಿ ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣ ಕಾಗದರಹಿತ ಆಸ್ತಿ ನೋಂದಣಿ – ಅರ್ಜಿ ಸಲ್ಲಿಕೆ, ಲಾಭಗಳು & ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣ ಮಾರ್ಗದರ್ಶಿ

ಭಾರತ್-ವಿಸ್ತಾರ್ ಎಐ ಸಾಧನ: ರೈತರ ಕೃಷಿ ಸಮಸ್ಯೆಗೆ ಬೆರಳ ತುದಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಎಐ ಪರಿಹಾರ | ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣ ಮಾಹಿತಿ

Bengaluru in Trouble: ಐಟಿ ಬಿದ್ದರೆ ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು ಬೀಳುತ್ತೆ – ಸಂಕಷ್ಟದಲ್ಲಿ ನಮ್ಮ ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು

What Is the Investment Required for Mushroom Farming?

What Are the Best Mushrooms to Grow for Profit?

Union Budget 2026–27 Agriculture Initiatives: Transforming Indian Farming for Global Markets

Budget 2026 Agriculture Policy: Push for High-Value Crops but Farmers Still Struggle

ಭಾರತದಲ್ಲಿ ಮಣ್ಣಿನ ಆರೋಗ್ಯ: ಸುಸ್ಥಿರ ಕೃಷಿ ಮತ್ತು ಆಹಾರ ಭದ್ರತೆಗೆ ಅಡಿಪಾಯ

2025ರ ವಾಣಿಜ್ಯ ಧಾನ್ಯ ಕೃಷಿಯ ಹೊಸ ಆವಿಷ್ಕಾರಗಳು: ಸ್ಮಾರ್ಟ್ ನೀರಾವರಿ, ಗೊಬ್ಬರ ಮತ್ತು ಪ್ರೆಸಿಷನ್ ಸ್ಪ್ರೇಯರ್ಗಳು

ಕೇಸರಿ ಕೃಷಿಗೆ ಎಷ್ಟು ಹೂಡಿಕೆ ಅಗತ್ಯವಿದೆ?

ಕೇಸರಿ (Saffron) ಬೆಳೆಯಲು ಅತ್ಯುತ್ತಮ ಹವಾಮಾನ ಯಾವುದು?
How to Start Kesari (Saffron) Farming in India?



