Latest News
Smart Farming and Agri-Tech | Solutions to the Growing Food Demand Crisis1

Overview of Blog
Agri-Tech and smart farming are transforming agriculture to satisfy the growing need for food worldwide. AI, IoT, automation, and precision farming are some of the technologies that help boost agricultural yields, enhance resource efficiency, and advance sustainability. A more resilient and environmentally friendly agriculture industry is ensured by innovations like drones, vertical farming, and climate-resilient crops. Future developments in AI, blockchain, and robots will propel the transformation of farming and guarantee global food security, despite obstacles like high costs, a lack of technical expertise, and connection problems.

Smart farming and Agri-Tech are transforming agriculture by combining automation, IoT, and AI to address the expanding food demand dilemma. Data-driven decision-making, drone technology, and precision farming are examples of innovations that maximize agricultural production while consuming the fewest resources possible. Food security over the long term is ensured by sustainable practices including climate-resilient crops and vertical farming. By assisting farmers in increasing production, lowering their environmental impact, and effectively meeting the growing need for food worldwide, these developments open the door to a more resilient and technologically advanced agricultural future.
Smart Farming’s Place in Contemporary Agriculture
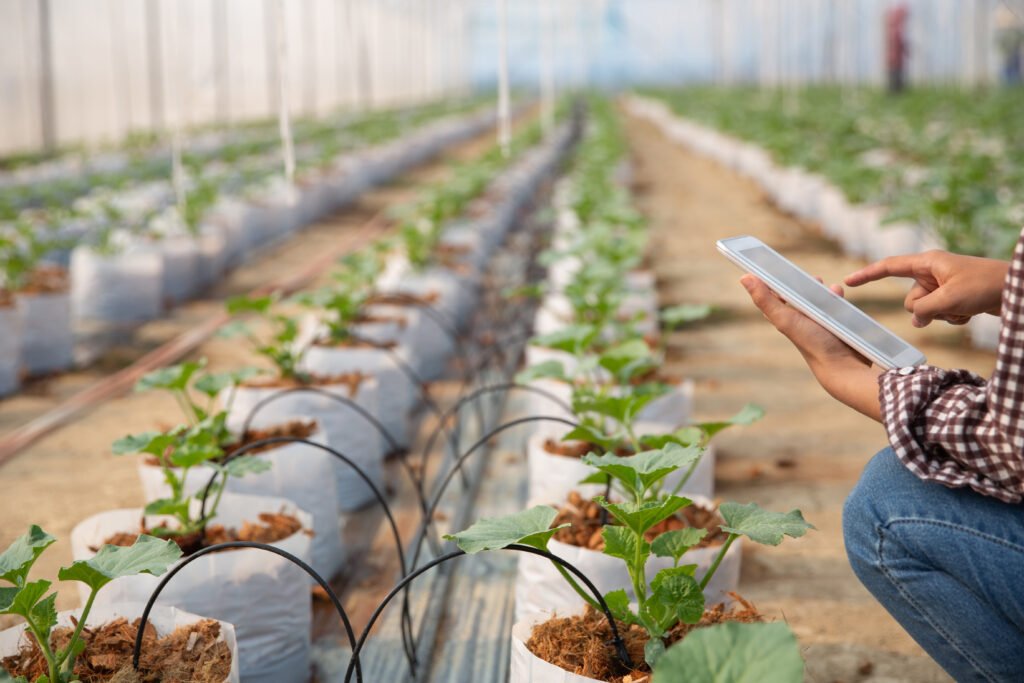
To maximize farming operations, smart farming makes use of cutting-edge technology including artificial intelligence (AI), robots, the Internet of Things (IoT), and precision agriculture. These developments aid farmers in increasing sustainability, minimising resource waste, and optimizing yields.

1. Accurate farming
To monitor and manage crops more effectively, precision agriculture uses data analytics, remote sensing, and GPS mapping. This method lowers expenses and the impact on the environment by allowing farmers to apply the proper amounts of water, fertilizer, and pesticides.
2. Smart Sensors Powered by IoT
Real-time information on crop health, weather, and soil moisture is provided via IoT-based sensors. Farmers may avoid problems like insect infestations, nutrient shortages, and excessive irrigation by keeping a close eye on these variables and making well-informed decisions.
3. Farming using AI and Machine Learning
With its ability to analyze massive information, forecast crop yields, and automate farming chores, artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly important in modern agriculture. Farming is becoming more efficient with the employment of AI-powered robots for automated crop monitoring, pest management, and harvesting.
Innovations in Agri-Tech Revolutionizing the Production of Food
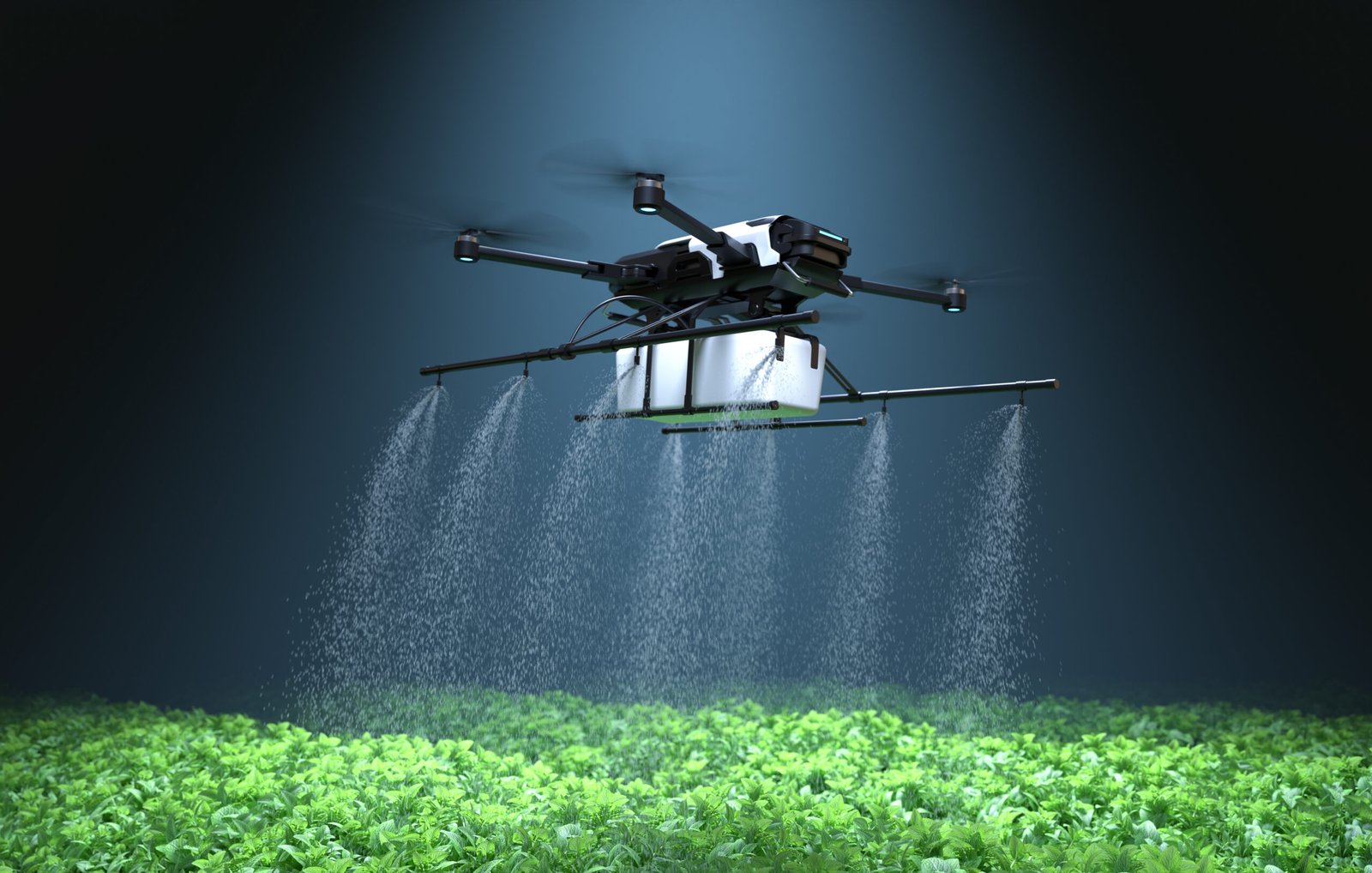
1. The use of drones
High-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors on drones assist farmers in crop monitoring, disease detection, and irrigation optimization. Accurate insights are provided by these aerial gadgets, which decrease manual labor and increase production.
2. Indoor and Vertical Farming
Vertical farming and indoor hydroponic systems provide creative solutions to produce crops in controlled settings on a limited amount of fertile land. These systems effectively produce food all year round, particularly in urban locations, using temperature control, nutrient-rich water solutions, and LED illumination.
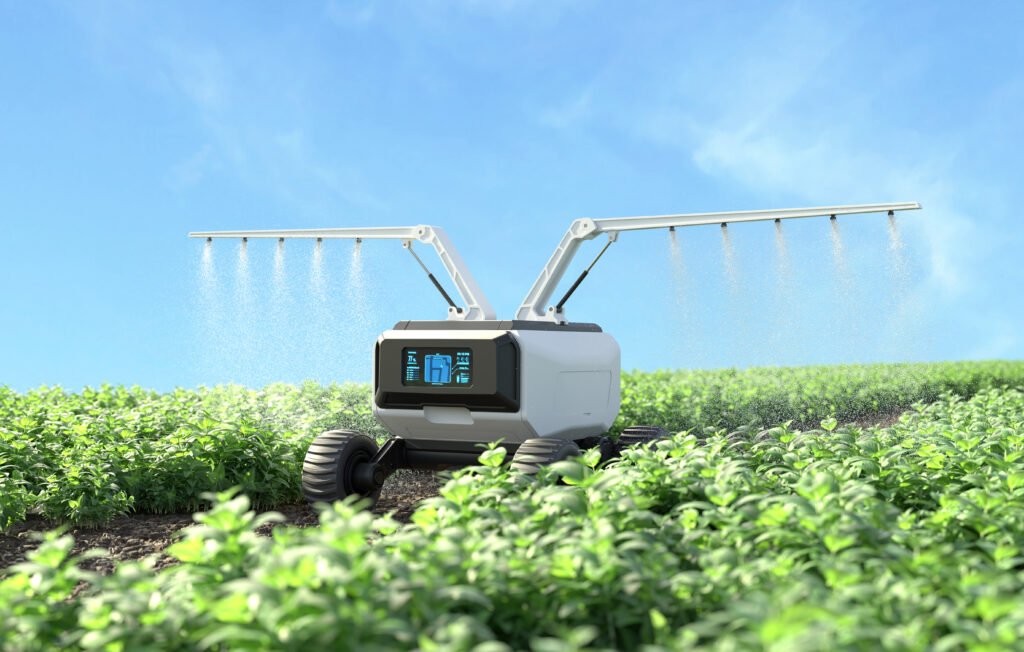
3. Robotics and Automated Machinery
Agricultural operations are made more efficient by automated irrigation systems, robotic harvesters, and smart tractors. These devices increase productivity, decrease the need for physical labor, and improve soil management, planting, and harvesting accuracy.
4. Crops Adaptable to Climate Change
High-yielding crop types that are resistant to pests and drought have been developed thanks to genetic engineering and biotechnology. These crops enable farmers to produce more food and adjust to the changing environment.
Advantages of Agri-Tech and Smart Farming
1. Higher yields of crops
Farmers may improve crop quality and production by optimizing irrigation, fertilizer management, and planting schedules via the use of data analytics, precision farming, and AI-driven insights.
2. Efficiency of Resources
By minimizing water, fertilizer, and pesticide waste, smart farming ensures resource efficiency and lessens environmental harm.
3. Diminished Effect on the Environment
Sustainable farming methods including organic farming, no-till farming, and precise resource application are encouraged by technological developments in agriculture, which also serve to lessen soil degradation and carbon footprints.
4. Increased Food Safety
By boosting yields and strengthening farming’s resistance to climate change, smart farming provides constant and dependable food supply in response to the world’s growing food need.
Implementing Agri-Tech and Smart Farming Presents Difficulties
- Despite its promise, a number of obstacles prevent smart farming from being widely used:
- High Initial Costs: Advanced Agri-Tech solutions are out of reach for many small-scale farmers.
- Lack of Technical Knowledge: To use smart agricultural technology efficiently, farmers must have the right training.
- Connectivity Problems: The internet infrastructure required for IoT-based farming solutions is sometimes lacking in rural regions.
- Data Privacy Issues: To safeguard farmers’ interests, stringent laws are needed for the gathering and use of agricultural data.
Smart Farming’s Future
- Governments, IT firms, and agricultural associations must collaborate to offer farmers training programs, better digital infrastructure, and reasonably priced solutions in order to overcome these obstacles.
- Among the upcoming developments in smart farming are:
- predictive analytics powered by AI to foresee agricultural illnesses and maximise harvests.
- Blockchain technology to guarantee fair trade and enhance food traceability.
- Harvesting, weeding, and planting are all done by autonomous agricultural robots.
- 5G-enabled smart farming to improve decision-making and data collecting in real time.
Conclusion
Smart farming and Agri-Tech are transforming agriculture by increasing its sustainability, efficiency, and ability to provide the world’s growing food needs. The future of food production will be driven by creative ideas as technology develops further, guaranteeing environmental protection and global food security. Farmers may increase output, cut waste, and build a more resilient agricultural sector by adopting these innovations.